3.9 KiB
Large lists in Clixon
Background
CIixon can handle large configurations. Here, large number of elements in a "flat" list is presented. There are other scaling usecases, such as large configuratin "depth", large number of requesting clients, etc.
Overview
The basic case is a large list, according to the following Yang specification:
container x {
description "top-level container";
list y {
description "List with potential large number of elements";
key "a";
leaf a {
description "key in list";
type int32;
}
leaf b {
description "payload data";
type string;
}
}
}
where a is a unique key and b is a payload, useful in replace operations.
XML lists with N elements are generated based on
this configuration, eg for N=10:
<y><a>0</a><b>0</b></y>
<y><a>1</a><b>1</b></y>
<y><a>2</a><b>2</b></y>
<y><a>3</a><b>3</b></y>
<y><a>4</a><b>4</b></y>
<y><a>5</a><b>5</b></y>
<y><a>6</a><b>6</b></y>
<y><a>7</a><b>7</b></y>
<y><a>8</a><b>8</b></y>
<y><a>9</a><b>9</b></y>
Requests are either made over the whole dataset, or for one specific element. The following example shows a Restconf GET operation of a single element:
curl -X GET http://localhost/restconf/data/scaling:x/y=3
{"scaling:y": [{"a": 3,"b": "3"}]}
Operations of single elements (transactions) are made in a burst of random elements, typically 100.
Tests
All details of the setup are in the test script.
Testcases
All tests measure the "real" time of a command on a lightly loaded
machine using the Linux command time(1).
The following tests were made (for each architecture and protocol):
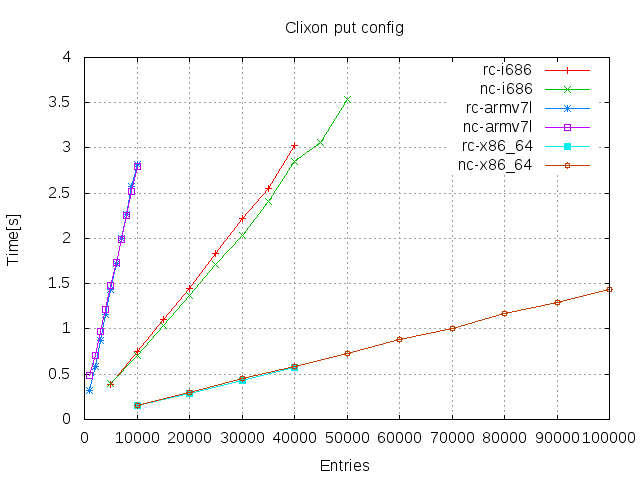
- Write
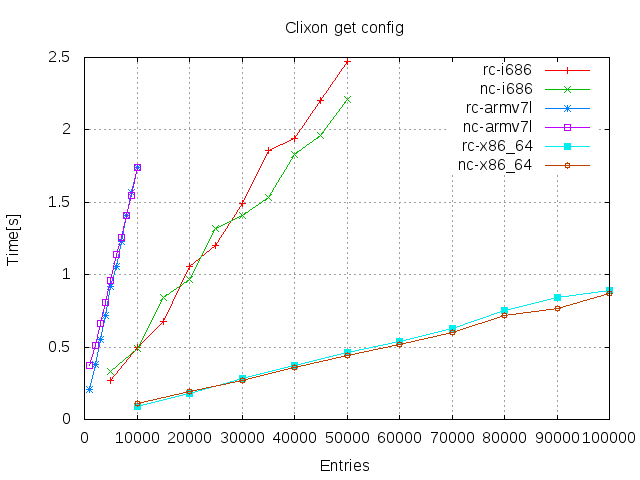
Nentries in one single operation. (With an empty datastore) - Read
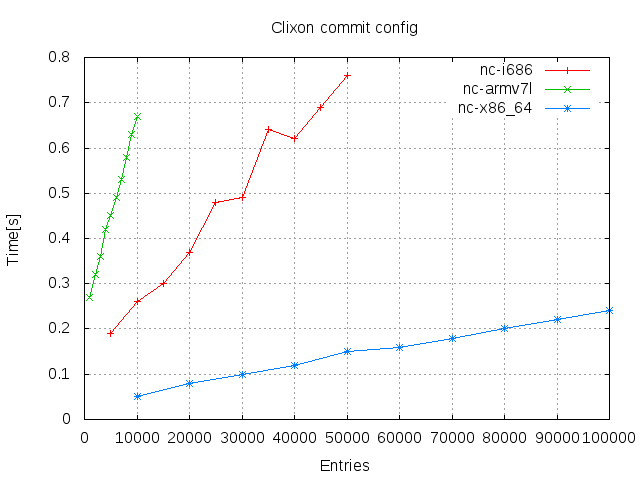
Nentries in one single operation. (With a datastore ofNentries) - Commit
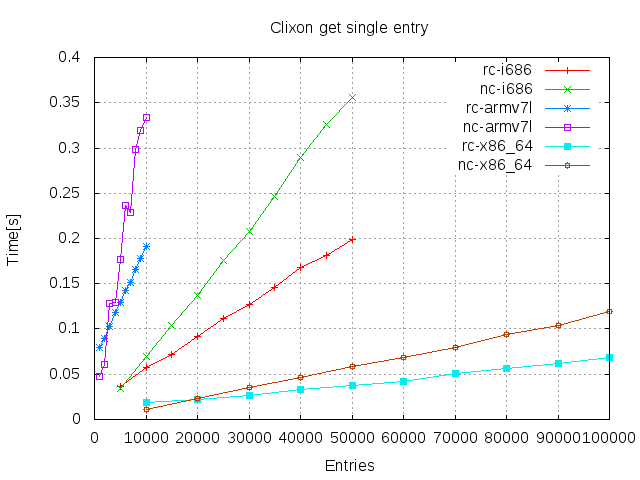
Nentries (With a candidate ofNentries and empty running) - Read 1 entry (In a datastore of
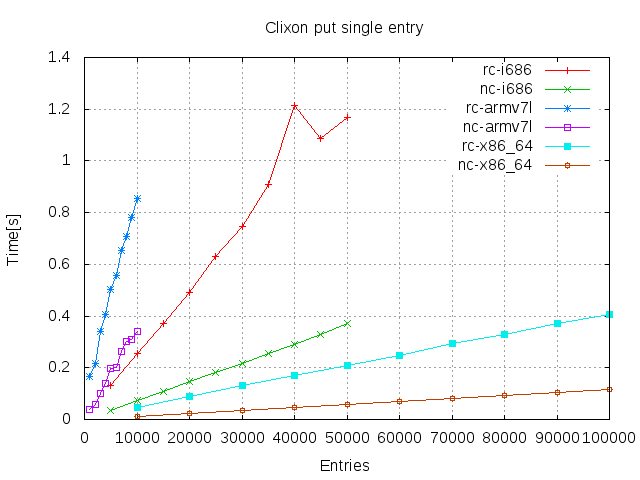
Nentries) - Write/Replace 1 entry (In a datastore of
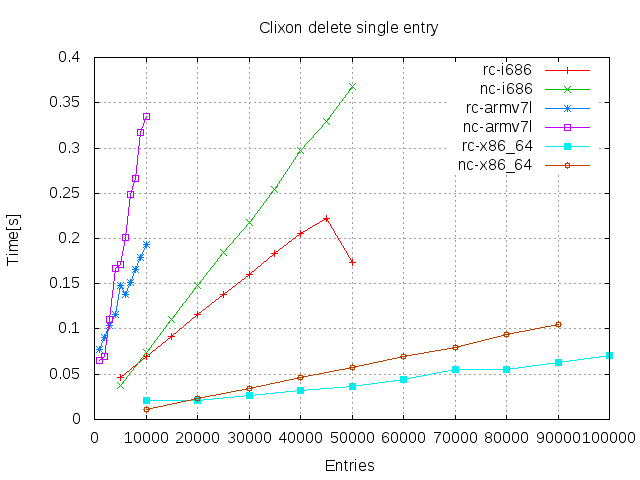
Nentries) - Delete 1 entry (In a datastore of
Nentries)
The tests are made using Netconf and Restconf, except commit which is made only for Netconf.
Architecture and OS
The tests were made on the following hardware, all running Ubuntu Linux:
- i686: dual Intel Core Duo processor (IBM Thinkpad X60)
- arm: ARMv7 Processor rev 5 (v7l) (Raspberry PI 2 Model B)
- x86-64: Intel Quad-core I5-8259U (Intel NUC Coffee Lake)
i686: Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS
Linux version 4.4.0-143-generic (buildd@lgw01-amd64-037) (gcc version 5.4.0 20160609 (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.10) ) #169-Ubuntu SMP Thu Feb 7 07:56:51 UTC 2019
Arm : Raspbian GNU/Linux 9
Linux version 4.14.79-v7+ (dc4@dc4-XPS13-9333) (gcc version 4.9.3 (crosstool-NG crosstool-ng-1.22.0-88-g8460611)) #1159 SMP Sun Nov 4 17:50:20 GMT 2018
x86_64: Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS
inux version 4.15.0-47-generic (buildd@lgw01-amd64-001) (gcc version 7.3.0 (Ubuntu 7.3.0-16ubuntu3)) #50-Ubuntu SMP Wed Mar 13 10:44:52 UTC 2019
Results
Discussion
References
RFC6241 "Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF)" RFC8040 "RESTCONF Protocol" i686 plot_perf.sh Test script