[](https://travis-ci.org/clicon/clixon)
# Clixon
Clixon is a YANG-based configuration manager, with interactive CLI,
NETCONF and RESTCONF interfaces, an embedded database and transaction
support.
* [Background](#background)
* [Frequently asked questions (FAQ)](doc/FAQ.md)
* [Hello world](example/hello/README.md)
* [Changelog](CHANGELOG.md)
* [Installation](#installation)
* [Licenses](#licenses)
* [Support](#support)
* [Dependencies](#dependencies)
* [Extending](#extending)
* [Yang](#yang)
* [CLI](doc/CLI.md)
* [XML and XPATH](#xml)
* [Netconf](#netconf)
* [Restconf](#restconf)
* [Datastore](datastore/README.md)
* [Authentication](#auth)
* [NACM Access control](#nacm)
* [Example](example/README.md)
* [Runtime](#runtime)
* [Clixon project page](http://www.clicon.org)
* [Tests and CI](test/README.md)
* [Scaling: large lists](doc/scaling/large-lists.md)
* [Containers](docker/README.md)
* [Roadmap](doc/ROADMAP.md)
* [Reference manual](#reference)
## Background
Clixon was implemented to provide an open-source generic configuration
tool. The existing [CLIgen](http://www.cligen.se) tool was for command-lines only, while Clixon is a system with configuration database, xml and rest interfaces all defined by Yang. Most of the projects using Clixon are for embedded network and measuring devices. But Clixon can be used for other systems as well due to its modular and pluggable architecture.
Users of Clixon currently include:
* [Netgate](https://www.netgate.com)
* [CloudMon360](http://cloudmon360.com)
* [Grideye](http://hagsand.se/grideye)
* [Netclean](https://www.netclean.com/solutions/whitebox) # only CLIgen
* [Prosilient's PTAnalyzer](https://prosilient.com) # only CLIgen
See also [Clicon project page](http://clicon.org).
Clixon runs on Linux, [FreeBSD port](https://www.freshports.org/devel/clixon) and Mac/Apple. CPU architecures include x86_64, i686, ARM32.
## Installation
A typical installation is as follows:
```
configure # Configure clixon to platform
make # Compile
sudo make install # Install libs, binaries, and config-files
sudo make install-include # Install include files (for compiling)
```
One [example application](example/README.md) is provided, a IETF IP YANG datamodel with
generated CLI, Netconf and restconf interface.
## Licenses
Clixon is open-source and dual licensed. Either Apache License, Version 2.0 or GNU
General Public License Version 2; you choose.
See [LICENSE.md](LICENSE.md) for the license.
## Dependencies
Clixon depends on the following software packages, which need to exist on the target machine.
- [CLIgen](http://github.com/olofhagsand/cligen) If you need to build and install CLIgen:
```
git clone https://github.com/olofhagsand/cligen.git
cd cligen; configure; make; make install
```
- Yacc/bison
- Lex/Flex
- Fcgi (if restconf is enabled)
## Support
Clixon interaction is best done posting issues, pull requests, or joining the
[slack channel](https://clixondev.slack.com).
[Slack invite](https://join.slack.com/t/clixondev/shared_invite/enQtMzI3OTM4MzA3Nzk3LTA3NWM4OWYwYWMxZDhiYTNhNjRkNjQ1NWI1Zjk5M2JjMDk4MTUzMTljYTZiYmNhODkwMDI2ZTkyNWU3ZWMyN2U).
## Extending
Clixon provides a core system and can be used as-is using available
Yang specifications. However, an application very quickly needs to
specialize functions. Clixon is extended by writing
plugins for cli and backend. Extensions for netconf and restconf
are also available.
Plugins are written in C and easiest is to look at
[example](example/README.md) or consulting the [FAQ](doc/FAQ.md).
## Yang
YANG and XML is the heart of Clixon. Yang modules are used as a
specification for handling XML configuration data. The YANG spec is
used to generate an interactive CLI, netconf and restconf clients. It
also manages an XML datastore.
Clixon follows:
- [YANG 1.0 RFC 6020](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc6020.txt)
- [YANG 1.1 RFC 7950](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7950.txt).
- [RFC 7895: YANG module library](http://www.rfc-base.org/txt/rfc-7895.txt)
However, the following YANG syntax modules are not implemented:
- deviation
- action
- refine
The following restrictions on Yang exists:
- Yang extended Xpath functions: re-match, deref, derived-from, derived-from-or-self, enum-value, bit-is-set
- Submodules cannot re-use a prefix in an import statement that is already used for another imported module in the module that the submodule belongs to. (see https://github.com/clicon/clixon/issues/60)
- Default values on leaf-lists are not supported (RFC7950 7.7.2)
## XML
Clixon has its own implementation of XML and XPATH implementation.
The standards covered include:
- [XML 1.0](https://www.w3.org/TR/2008/REC-xml-20081126)
- [Namespaces in XML 1.0](https://www.w3.org/TR/2009/REC-xml-names-20091208)
- [XPATH 1.0](https://www.w3.org/TR/xpath-10)
Not supported:
- !DOCTYPE (ie DTD)
Historically, Clixon has not until 3.9 made strict namespace
enforcing. For example, the following non-strict netconf was
previously accepted:
```
```
In 3.9, the same statement should be, for example:
```
```
Note that base netconf syntax is still not enforced but recommended:
```
```
## Netconf
Clixon implements the following NETCONF proposals or standards:
- [RFC 6241: NETCONF Configuration Protocol](http://www.rfc-base.org/txt/rfc-6241.txt)
- [RFC 6242: Using the NETCONF Configuration Protocol over Secure Shell (SSH)](http://www.rfc-base.org/txt/rfc-6242.txt)
- [RFC 5277: NETCONF Event Notifications](http://www.rfc-base.org/txt/rfc-5277.txt)
- [RFC 8341: Network Configuration Access Control Model](http://www.rfc-base.org/txt/rfc-8341.txt)
The following RFC6241 capabilities/features are hardcoded in Clixon:
- :candidate (RFC6241 8.3)
- :validate (RFC6241 8.6)
- :xpath (RFC6241 8.9)
- :notification: (RFC5277)
The following features are optional and can be enabled by setting CLICON_FEATURE:
- :startup (RFC6241 8.7)
Clixon does not support the following netconf features:
- :url capability
- copy-config source config
- edit-config testopts
- edit-config erropts
- edit-config config-text
- edit-config operation
Some other deviations from the RFC:
- edit-config xpath select statement does not support namespaces
## Restconf
Clixon Restconf is a daemon based on FastCGI C-API. Instructions are available to
run with NGINX.
The implementatation is based on [RFC 8040: RESTCONF Protocol](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8040).
The following features are supported:
- OPTIONS, HEAD, GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
- stream notifications (RFC8040 sec 6)
- query parameters start-time and stop-time(RFC8040 section 4.9)
The following features are not implemented:
- PATCH
- query parameters other than start/stop-time.
See [more detailed instructions](apps/restconf/README.md).
## Datastore
The Clixon datastore is a stand-alone XML based datastore. The idea is
to be able to use different datastores backends with the same
API. Currently only an XML plain text datastore is supported.
The datastore is primarily designed to be used by Clixon but can be used
separately.
See [more detailed instructions](datastore/README.md).
## Auth
Authentication is managed outside Clixon using SSH, SSL, Oauth2, etc.
For CLI, login is typically made via SSH. For netconf, SSH netconf
subsystem can be used.
Restconf however needs credentials. This is done by writing a credentials callback in a restconf plugin. See:
* [FAQ](doc/FAQ.md#how-do-i-write-an-authentication-callback).
* [Example](example/README.md) has an example how to do this with HTTP basic auth.
* It has been done for other projects using Oauth2 or (https://github.com/CESNET/Netopeer2/tree/master/server/configuration)
The clients send the ID of the user using a "username" attribute with
the RPC calls to the backend. Note that the backend trusts the clients
so the clients can in principle fake a username.
## NACM
Clixon includes an experimental Network Configuration Access Control Model (NACM) according to [RFC8341(NACM)](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8341).
To enable NACM:
* The `CLICON_NACM_MODE` config variable is by default `disabled`.
* If the mode is internal`, NACM configurations are expected to be in the regular configuration, managed by regular candidate/runing/commit procedures. This mode may have some problems with bootstrapping.
* If the mode is `external`, the `CLICON_NACM_FILE` yang config variable contains the name of a separate configuration file containing the NACM configurations. After changes in this file, the backend needs to be restarted.
The [example](example/README.md) contains a http basic auth and a NACM backend callback for mandatory state variables.
NACM is implemented in the backend with incoming RPC and data node access control points.
The functionality is as follows (references to sections in [RFC8341](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8341)):
* Access control point support:
* Incoming RPC Message validation is supported (3.4.4)
* Data Node Access validation is supported (3.4.5), except:
* rule-type data-node path is not supported
* Outgoing noitification aithorization is _not_ supported (3.4.6)
* RPC:s are supported _except_:
* `copy-config`for other src/target combinations than running/startup (3.2.6)
* `commit` - NACM is applied to candidate and running operations only (3.2.8)
* Client-side RPC:s are _not_ supported.
## Runtime
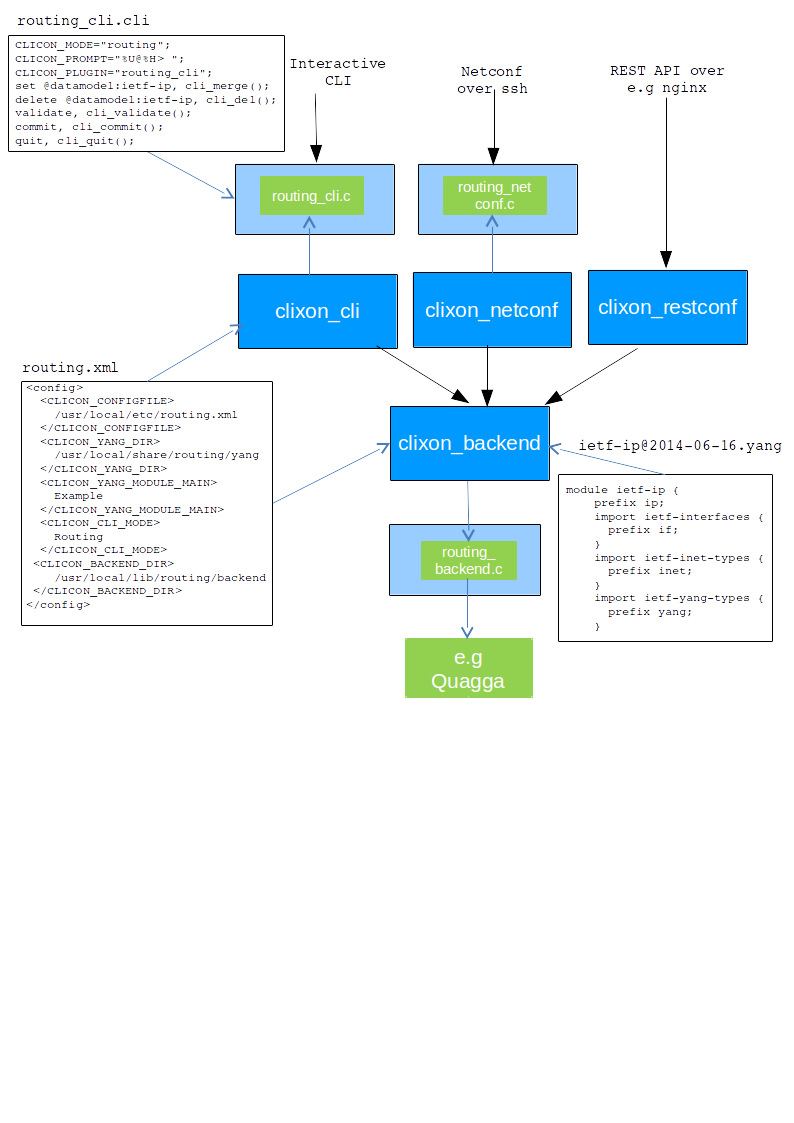 The figure shows the SDK runtime of Clixon.
## Reference
Clixon uses [Doxygen](http://www.doxygen.nl/index.html) for reference documentation.
You need to install doxygen and graphviz on your system.
Build it in the doc directory and point the browser to `.../clixon/doc/html/index.html` as follows:
```
> cd doc
> make doc
> make graphs # detailed callgraphs
```
The figure shows the SDK runtime of Clixon.
## Reference
Clixon uses [Doxygen](http://www.doxygen.nl/index.html) for reference documentation.
You need to install doxygen and graphviz on your system.
Build it in the doc directory and point the browser to `.../clixon/doc/html/index.html` as follows:
```
> cd doc
> make doc
> make graphs # detailed callgraphs
``` The figure shows the SDK runtime of Clixon.
## Reference
Clixon uses [Doxygen](http://www.doxygen.nl/index.html) for reference documentation.
You need to install doxygen and graphviz on your system.
Build it in the doc directory and point the browser to `.../clixon/doc/html/index.html` as follows:
```
> cd doc
> make doc
> make graphs # detailed callgraphs
```
The figure shows the SDK runtime of Clixon.
## Reference
Clixon uses [Doxygen](http://www.doxygen.nl/index.html) for reference documentation.
You need to install doxygen and graphviz on your system.
Build it in the doc directory and point the browser to `.../clixon/doc/html/index.html` as follows:
```
> cd doc
> make doc
> make graphs # detailed callgraphs
```